interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
: Regional Interest
List Grid Map
Found
76
- Showing :
61 - 76
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 23.8km (S) A small village built at an altitude of 540 m in the south parts of the mountain Dikti at the borders of the province of Ierapetra-Viannos. The imposing mountains above the village, the south horizon among the olive-covered hills and in the lower villages, the cool climate create in you a sensation of bodily and spiritual well-being at this balcony of the Cretan nature. Five settlements, two of them uninhabited today, constituted the Community of Riza, now a Local Department of the Municipality of Ierapetra.  Ierapetra, Lassithi at 24.7km (SE) One of the most beautiful parts of the hinterland of Ierapetra is occupied by the picturesque village of Kalamafka. It is situated on the edge of the Lassithi mountains, an area known for its impressive diversity in landscape. Kalamafka sits at an altitude of 480 meters, 15 kilometers from the town of Ierapetra and 25 kilometers from Agios Nikolaos. Kalamafka is a picturesque, large, and prosperous village surrounded by unique natural beauty. The springs at Kefalovryso, with its plane trees and lush vegetation, as well as its old historical churches, gorges, and springs, attract visitors due to the oasis-like coolness it offers in this otherwise dry and hot region. The village's wealth lies in its water sources and the vitality of its residents, who resist urbanization. Another reason for Kalamafka's enduring population is its advantageous location, as it is centrally positioned between the north and south coasts of the island, drawing daily visitors from Ierapetra and Agios Nikolaos. History: The village derives its name from "Kali Afkla," a wooden channel that was once used to transfer water from one riverbank to another at the springs of Kefalovryso. Another explanation for the name is that the rock formation on Kastelos Hill resembles a Greek Orthodox priest's hat (kalymafki). Kalamafka, known as ancient Larisa, has been inhabited since the Minoan era. In the Psathi area, along the road to Ierapetra, archaeological findings such as human skulls, clay pots, spearheads, and various grave goods from the sub-Minoan era have been discovered. The geographer Strabo mentions Kalamafka, ancient Larisa, as follows: "And in Crete there is the city of Larisa, which now is united with Ierapytna, and from which the plain below, called Larision, takes its name." The god protector of ancient Larisa was Asclepius, and this is why the Medical Association of Lassithi has adopted the figure of a statuette discovered on the Kastelos peak, which overlooks the village and served as a peak sanctuary according to Mr. Michalis Pytikakis. Larisa was conquered around the 3rd century B.C. by Ierapytna, and its residents were relocated as per the terms of the treaty. Evidence from subsequent historical periods suggests that the Kalamafka area has been continuously inhabited due to the presence of the water sources of Kefalovryso. Place names like Kastelos, Mesokastela, and Larisakia attest to its historical significance. Kastelos Hill, serving as the seat of a feudal lord during the Venetian rule, had 435 residents in 1583. It boasted several notable Byzantine and post-Byzantine churches, along with numerous chapels. During the Turkish rule, it was a breeding ground for prominent chieftains like Nikolaos Foniadakis and Ioannis Baritakis. The village's history is marked by struggles and sacrifices that cannot be easily summarized. Today, Kalamafka is a vibrant village with a growing population. It has a two-seat school, a nursery school, a cultural association, numerous coffee houses, and seven taverns. The natural landscape, often referred to as "Chinese" due to its small rock pillars with bonsais, stone formations, and Kastelos Hill with its 224 steps, is considered a monument of natural history. Kalamafka offers visitors a wealth of attractions, including caves, rock paintings, the Havgas gorge, an ancient olive press, and the churches of Saint John and Saint Anthony. The taverns, shaded by plane trees and surrounded by running water, serve traditional and delicious local dishes, including the traditional "klostenios" halva and skyfomakarounes (local pasta). The sounds of the lyra, violin, and lute add to the ambiance, pleasing both locals and foreigners. There are indeed many compelling reasons to visit Kalamafka. By Toby Robert Image Library
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 24.7km (S) Mournies (GR: Μουρνιές - meaning: mulberry trees) is a village of the western Ierapetra. It is located north of Myrtos, and 25 kilometers away from Ierapetra at 275m (elevation), built on the southeastern outskirts of the Lasithi mountains, with beautiful views of the Libyan Sea and the plains of Ierapetra. It has a mild climate, without extremes, ideal both for permanent residence and for holidays. The landscape is hilly plenty of olive trees. In the 2001 census it had 83 residents. Mournies is a beautiful, historic, picturesque and traditional village with cafes, a square with a war memorial, an old fountain, and narrow streets branching off the main street of the village. Mournies was named after the Mulberry tree which however is not abundant in the area.  Ierapetra, Lassithi at 25.3km (S) A stately village built in settlements, 22 km away from Ierapetra, at an altitudeof 225 m, next to the Ierapetra-Vianos provincial road. A green landscape,overgrown with olive trees, with an unlimited view of the Libyan Sea, to thesurrounding areas Koleitos, Kakon Oros, to the beaches Vatos and Kallikovrechtis.An almost abandoned village, with old houses built of stone, with chiseled doorframes and coats of arms bearing the Christian cross and proving its old gloryand history.Giannis Dimitromanolakis, an author from Gdohia, writes:“Gdohia sprouted right opposite the beach of the Libyan Sea. Nothing wouldhave been better for the pirates, who, like diabolical ghosts, emerged into thenight to kill and prey. The village’s history is dipped in blood, as it often sufferedfrom the raids of the pirates from the Barbary Coast. It took the name Gdohiafrom the catastrophes, from the verb “gdyno”, to skin, to set fire, to devastate.”Gdohia’s course in time has evidence of struggles, sacrifices and holocausts toshow. It was not only exposed to the pirates but it was situated on the naturalsouth passage going from the Viannos area to the Ierapetra area. This meantthat the hordes of barbarous conquerors burnt and devastated it, along withthe other Symiana villages, as they are called, in the West Ierapetra.Gdohia’s settlements are built leaving a distance between each other: KatoGdohia or Pitropiana, taking their name from the Epitropakis family livingthere, Pefkiana or Grysboliana, from the Grysbolakis family, Dimitromanolianafrom the Dimitromanolakis family, Daskaliana from the Daskalakis family,Papadiana from the Papadakis family. Great stonecutters, stoneworkers,famous for their art, Gdohia’s residents built the mansions of the whole areaand the famous bridge of Myrtos using stones from the quarries of Kolleitos.The miraculous church of Panagia (Our Lady) Evaggelistria of Gdohia, a workof art and a great ecclesiastical monument is also built by Gdohia’s residents.Gdohia village, once the seat of a Community, today a Local Department ofthe Municipality of Ierapetra, presents an exceptional sight-seeing interest. Itprovides natural landscapes, beautiful beaches, picturesque little churches onthe hills, a spacious square with palm trees, seats and a war memorial forthe fallen fighters of the liberation wars. In the 1881 census, 296 residents areregistered and 73 in 2001. Gdohia’s permanent residents, along with someforeigners’ families who have bought and renovated old houses, struggle forthe village’s development which gradually acquires the necessary infrastructures.A village with rich history and civilization, with vast olive groves, a nicemild climate, both during summer and winter, it hopes to come back to life.The old mansions, half-wrecked and burned in the German Occupation, standas if they were sculptures, a painting with the deep blue Libyan Sea serving asa background, narrate the flourishing, the glory and the history of Gdohia andwait to be inhabited again.
 Elounda, Mirabello bay, Lassithi at 25.5km (E) The island of Spinalonga (Gr: Σπιναλόγκα), officially known as Kalydon (Καλυδών), is located in the Gulf of Elounda in north-eastern Crete, in Lasithi prefecture, next to the town of Elounda. The official Greek name of the island today is Kalydon. Originally, Spinalonga was not an island, it was part of the island of Crete. During Venetian occupation the island was carved out of the coast for defense purposes and a fort was built there. A popular name for the island since Venetian rule is Spinalonga. During Venetian rule, salt was harvested from salt pans around the island. The island has also been used as a leper colony. Spinalonga has appeared in novels, television series, and a short film.
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 26.2km (SE) The village of the rising sun, as its name declares. The golden rays illuminate Anatoli, the hanging rocks, the Holy Cross church, Drygies, Karkasa, and give the impression that the sun keeps rising. It is an old, historical, traditional village, situated at 17 km in the north-west of Ierapetra, at an altitude of 600 m. Its housesare visible from the plain and seem like white doves, nested in the fortified mountain of Anatoli. A privileged place, it has been a cradle of men of letters, Notaries, University professors, with great history and civilization.In the 70s, most of Anatoli’s residents got down to the plain and worked in the glasshouse cultivations. They founded, along with residents from other villages the settlementsStomio, Nea Anatoli, Ammoudares. The small picturesque village Kalogeroi, which, according to tradition, was built by a Turkish Aga, is part of Anatoli. It is referenced sincethe era of the Venetian rule. In 1583, along with Kalogeroi, it had 666 residents. In 1951 it had 897 and in 2001, along with Nea Anatoli, it had 1235 residents. The Tower of theVenetian feudal lord still lies in ruins in the north of the village. It nurtured important men of letters, such as Antonios Damilas, scribe and printer, Neilos Damilas, scholarlypriest-monk in the Karkasia Monastery, Dimitrios Damilas, brother of Antonios, scribe and printer in Milan, who published the “Greek Grammar” in 1476, Anthimos Donos,and Ioannis Olokalos, whose notary documents have been recently published. The latter had his seat in Drygies, a wonderful location in the east of the village with runningwaters, a tavern with a view of Ierapetra and the little church of Saint Foteini. Anatoli was an important intellectual center, having a school during the Venetian rule and a secretschool during the Turkish rule.The area of Anatoli, a fortified position, produced great fighters during the Turkish rule, such as Emmanuel Lakerdas, general chief of Ierapetra, Iakovos Mahairas, AthanasiosBarberakis and Georgios Bekiaris.Its history and struggles were imortant in all the historical periods. It has many ecclesiastical monuments, Monasteries and Byzantine icons of great art.The old traditional settlement of Anatoli has remained untouched by time, with its stone-built houses, the alleys, the old Kato Vrysi. Five years ago, it entered a program ofrenovation, was characterized as a traditional settlement and today houses and tourist lodgings of exceptional esthetics are built in stone. In a few years, Anatoli of Ierapetra willbe one of the most beautiful villages of Crete, with its wonderful climate, its extraordinary view, its incomparable natural landscape on which the Museum of Natural Historyof Crete has worked and about which it published a relevant document.Anatoli as well as its residents have to this day been successful in the agricultural, tourist and intellectual sectors. Personalities coming from the village dominate the political,social and intellectual life of our country. Anatoli was a Municipality in the beginning of the 20th century, then a Community and today a Local Department ofthe Municipality of Ierapetra, building its future on solid foundations. Hosting important cultural events, with itshistorical, folkloric and musical contributions, it is a center of attraction of bothlocals and foreigners. With two taverns, two coffee houses, a renovatedold school and hospitable residents, it satisfies the most demandingvisitors. Anatoli is even rich in snails and wild mushrooms.
 Iraklion at 26.7km (NW) This 2 km long sandy beach was for years and still is the favorite beach of the people of Heraklion town. It is named after the river "Karteros" which outflows at the west end of it near the airport. The water is clean, the seabed is sandy with smoothly shelving and swimming is safe. The access is free in most parts except for some areas that are reserved for military personnel and the municipal beach "Akti" where visitors should pay an entrance fee in order to use the facilities. At the east end there are some very good taverns offering fresh fish among their specialties and are very popular with locals and tourists alike.
Image Library
 Archanes, Iraklion at 27.4km (W) A small traditional town (~4000 people) 15 km south of Iraklion on the foot of the sacred mountain Yiouhtas. Renowned for its excellent wine (from the varieties: vilana, kotsifali and madilari) and the archaeolocical sites and caves. In 1912, Xanthoudides noted the importance of Archanes, but Sir Arthur Evans was the first to characterize the site as palatial, declaring that Archanes was likely a Summer Palace for the Knossos kings. Spyridon Marinatos and N. Platon excavated minor areas in the region, but nothing supported Evans' theory. In 1964, J. Sakellarakis dug trial trenches at the Tourkoyeitonia site and uncovered the first evidence of a palace site. Since 1966, Archanes has been excavated by the Greek Archaeaological Society under the supervision of John Sakellarakis and Efi Sapouna-Sakellarakis. Links: http://www.archanes.gr/(GR) Image Library
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 27.6km (SE) Myrtos (GR: Μύρτος) is situated 15km to the west of Ierapetra, at the estuaries of the river Sarantapihos, in a valley with olive and orange trees. It is a beautiful village built by the sea, with a beach street lined with taverns and cafe bars. In a short distance from Myrtos on a low hill lies the archaeological site of "Pyrgos" with the ruins of a villa from the post minoan period and a little further at "Fournou Koryfi" lie the ruins of a proto minoan settlement. Myrtos features a small archaeological museum with exhibits mostly from the area, an initiative of a local teacher. Myrtos is a popular tourist destination, with nice small hotels, picturesque taverns and kafeneions, a lovely sandy beach and hospitable people. Image Library
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 27.7km (SE) Between OLEROS and OLERIA there is the village Meseleroi, which took its name from the ancient OLEROS. It is situated at 10 km in the north of Ierapetra at an altitude of 360 m. Ancient Oleros flourished during the classical times, to be conquered by thepowerful Ierapytna. Oleria was a place of worship for Oleria Athena, with its famous statue, venerated by the residents of Oleria and Ierapytna.  Archanes at 28km (W) Excavations at Phourni have brought to light 26 buildings, most of which had funerary use. The cemetery was used from 2400 B.C. until 1200 B.C. and each complex had more than one architectural phase. Most of the funerary buildings were used for many decades and contain successive burials. Excavations were begun in 1964 by Efi and John Sakellarakis and have been continued until today (1995) with short interruptions. Most of the buildings are preserved in good condition.  Palace and Archaeological site at 28.5km (W) The famous Palace of king Minos and the centre of the Minoan civilisation 5km south of Iraklion. The Great Palace covered an area of 20.000 sq. meters and had 1.400 rooms. Every section of the Palace had a specific use. In the west side of the Palace were the chambers of the ceremonies, of the administration and of the public storehouse...
Image Library
 Archanes at 28.9km (W) The Minoan villa at Vathypetro was most likely the residence of a local ruler. Its architecture is comparable to that of a "Little Palace": it has a central and west court, a small tripartite shrine, a three-columned portico, storerooms and workshops. It seems that the construction of the building was never completed. Interesting elements of its architecture are the installations of a wine-press in the south wing and an oil-press in the courtyard.  Iraklion ( Nea Alikarnassos) at 29km (NW) Heraklion International Airport, "Nikos Kazantzakis" (Greek: Κρατικός Αερολιμένας Ηρακλείου, "Νίκος Καζαντζάκης") or Nikos Kazantzakis International Airport (IATA: HER, ICAO: LGIR) is the primary airport on the island of Crete, Greece. It is located about 5km from the main city of Heraklion. Heraklion International Airport is is one of the biggest in Greece and receives approximately 15% of the total tourist traffic of Greece. There are many airlines currently operating flights from Athens and Thessaloniki to Iraklion (Olympic Airways, Aegean Airlines and others), while during the high season there are flights from/to Rhodes, Mykonos, Santorini and other Greek islands. There are also international airlines that connects Iraklion to other European cities. During the summer season there are numerous chartered flights to Iraklion from all over Europe (mainly Germany, the United Kingdom, Russia, and Holland). During the summer months there is a huge increase in air traffic that peaks in August (approximately 130 flights per day). Major car-rental companies have desks at the airport. Taxi and public bus are available for transfer from/to Iraklion.  Archanes at 29.4km (W) Anemóspilia (GR: Aνεμόσπηλια). Anemospilia is an archeological site at the northern foot of Mount Yuchtas, in the prefecture of Heraklion in Crete. A rectangular building has been found which dates from the Minoan era and was destroyed by an earthquake in the 17th century BC. The building with three narrow chambers, each opening into a long corridor to the north, which extends along the whole width of the building. The area is enclosed with a stone wall and the whole structure has been interpreted as a shrine; in the central room was found a "xoanon" (statue) of the deity worshiped here. In the west room, where the altar stood, was uncovered, according to the excavator, the first human sacrifice to have ever taken place in Minoan times. (although this view has been challenged). The building at Anemospelia was used for only half a century, as it was suddenly destroyed by an earthquake in the middle of the 17th century B.C. The site was excavated in the summer of 1979 by John Sakellarakis.   Aerial view 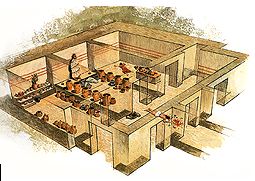 Shrine model Links: Minoan Religion (Foundation of the Hellenic World)  Ierapetra, Lassithi at 29.6km (SE) It is a small village, 7 km to the north of Ierapetra, at an altitude of 212 m. According to tradition, the village took its name from a large olive tree. It produced at least 10 sacks of olives and it provoked admiration by its size, and mostly by its height (Makrylia meaning tall olive tree). The village is old and traditional, with original Cretan style houses that have remained untouched over the time, in a beautiful and healthy environment, with a view of the overgrown with olive trees plain, with a rich history and hospitable residents. |
||
|
| ||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S


