interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
126
- Showing :
21 - 40
 Kenourgiou, Iraklion at 14.7km (E) Priniás (GR: Πρινιάς) is a small village located 35km southwest of Iraklion town and 4km from Agia Varvara, at a height of 610 m above sea level. The village of Prinias lies on the border of three regions: Malevizi, Kenouriou and Monofatsi, and is recorded as forming part of all three regions in the censi.  Voroi, Messara, Iraklion at 15.3km (S) The exhibited objects in the Museum come from all over Crete. These objects show that the folk culture of Crete is characterized by an amalgam of influences in which Minoan (2000-1000 BC), Archaic (1000-500 BC) and Byzantine models prevail, especially in agriculture, stock breeding, pottery and basketry.
 Mires, Messara Valley at 15.3km (S) It is located north of Mires close to a small gorge, with springs and covered with trees. There are many churches in the village the most important one being the church of Agios Nikolaos, a domed church dated to the 13th century. The walls of the temple are hand painted with biblical scenes and pictures of saints
 Messara, Iraklion South at 15.7km (S) Vori is a beautiful, traditional village of the county of Pirgiotissas in the Messara Valley. It is located 60 km south of Iraklion and in the western part of the Messara Valley. The village stretches in a slope, by the side of a small river. The archaeological site of Phaistos is 2 km to the south and the coast of Messara 4 km to the west.
Monastiraki (The archaeological site) Amari at 15.7km (W) Monastiraki lies in the valley of Amari, on the natural route leading from northern Crete to the Messara plain. Excavations have brought to light a centre of the Old Palace period (1950-1700 B.C.). which was destroyed by fire following an earthquake. The large number of storerooms and the existence of two archive rooms with many clay sealings indicate a palatial character for the site. Other finds on the top of a neighbouring hill suggest there must have been a religious centre in the area, as well. Image Library
 Messara, Iraklion South at 16.2km (SW) The town of Timpaki (GR: Τυμπάκι) is located in the west edge of the plain of Messara, 65.3km away from the city of Iraklion. It is a rich and busy town with significant economic activity especially due to the early vegetables production in the wider area. There are banks, a post office, medical centers, stores, schools, hotels, restaurants, ect to cover both the needs of the locals and visitors.
 Malevizi, Iraklion at 16.2km (E) Pyrgou lies 20 km from Iraklion and 1km from Agios Myron at 400m a.s.l with 354 inhabitants. It is built on a hillside overlooking the area, with panoramic view to the village of Kroussonas and the ravine of "Agia Irini". At the village's perimeter there are well maintained tower-like houses.  Kenourgiou, Iraklion at 16.4km (SE) Agia Varvára (GR: Αγία Βαρβάρα) is a town built along the road between the Messara plain and the Malevizi region at the highest point (580 m). The town enjoys a unique location with a splendid view into the Malevizi region, and a cool climate, particularly pleasant during the hot summer months. It produces first-rate fruit and vegetables. Because of its strategic location on the main north-south axis, the town was often exposed to fierce battles. A famous warrior, Mathiou Kapitakis or Mathioudakis was born here: he fought side to side with Karaiskakis and was killed at Faliro. His comrade-in-arms, Logios, was the hero of Aghios Thomas. As you reach the village, on the north side there is a rock with a chapel dedicated to Profitis Ilias. On this rock -which used to be twice as large but part of it fell off at the beginning of the 19th century- there used to be an ancient temple. Nowadays, the visitor can find every kind of commodity and facility on hand at the modern town of Aghia Varvara. In summer a special 'tsikoudia' feast, and in early spring a carnival feast are organized by the Cultural Association of the town. At the centre of the town, there are two churches - one old and one new - both dedicated to the patron saint, Aghia Varvara. Three Byzantine churches are also well worth a visit: Profitis Ilias, Aghios Giorgos and Aghios Ioannis, and of course the old monastery of Aghia Pelagia by the cemetery.  Messara bay, Iraklion South at 16.5km (SW) Kokkinos Pirgos (GR: Κόκκινος Πύργος) is a small coastal community, 2km away from Timbaki with a nice, long sandy beach, one of the longest in Crete, and a clear transparent sea. The part of the beach to the north west of the harbour is called Makrimaliana (or Kakoskalo) and the south east part of it is called Katalyki . The harbour in front of the village of Kokkinos Pirgos, offers docking facilities for sailing and fishing boats. There are hotels, restaurants, bars, etc. across the harbour and along the beach. You can always find good fresh fish in the taverns of the village. Kokkinos Pirgos (meaning red tower) , took its name from a castle that use to be there during the Middle Ages, which was built by red clay earth.
Image Library
 Mylopotamos, Rethymno at 16.7km (N) Apladianá (GR: Απλαδιανά) is a small village built at the foot of the two Kouloukona heights. The settlement stretches out along the old national road, where it developed after the opening of the new national road. It comprises cafes, tavernas, and accommodation facilities included in the Countryside Tourism programs. It is worth your while, however, to visit the old village, climbing there on foot or by car. Picturesque, narrow streets, wonderful old houses with interesting architectural elements, old cisterns and churches will reward your efforts. The old village built on a height of 260 m above sea-level has 175 inhabitants and the settlement along the old national road, known as "Kampos ton Apladianon", has 78 inhabitants. It is 40 kilometres away from Rethymnon and is located at the foot of the highest peak of the Kouloukona mountain in the Tallaios range. Historical background Already as far back as 1368 we find a mention of the Aplada family, the founders of the present village and in the topographical maps of the Civil Engineering Services of Rethymnon it figures as Pladiana. The settlement is not mentioned in the 16th and 17th cent. documents. In the 1881 census, Apladiana is attributed to the commune of Garazo, with 57 inhabitants and in 1900 it is referred to as the Apladiana Commune which, together with the Cheliana settlement, had 153 inhabitants.  Archaeological Site in Messara, S-W Iraklion at 16.8km (S) The "Royal Villa" at Ayia Triada which is situated very close to Phaistos, was built in about 1550 BC. i.e. just before the new palace at Phaistos, and was destroyed by fire in l450 BC, like all other important Minoan centres. It succeeded the first palace at Phaistos as the economic and administrative centre of the regions depriving the new palace there of this role, and appears to have had connections with Knossos. The two wings, with an open-air space between them, consisted of groups of interconnecting rooms (polythyra), storerooms and stairways. On the site of the ruins, a Mycenaean megaron, the so-called "Agora" and an open - air shrine were subsequently built. In the villa's disaster layer from the fire in 1450 BC, excavation revealed a valuable group of exceptional works of art, precious materials, records in Minoan script and seals. The famous black serpentine vessels, the "Harvesters' Vase", the "Boxers' Vase" and the "Chieftain ‘ s Cup", the wall paintings depicting the natural landscape, the sarcophagus, the bronze and clay figurines of worshipers and the copper ingots from the Treasury are among the most noteworthy findings.  Moires, Messara at 17km (S) The monastery of Panagia Kaliviani is located at the 59th km on the road Iraklion-Phaistos. The monastery was built during the second Byzantine period. The small Byzantine chapel was painted with frescoes but most of them are today destroyed. The chapel was deserted until, during the Turkish occupation in 1873, an old small icon of the Annunciation of the Holy Mother was miraculously found there.and the monastery became a place of worship.  Kenourgiou, Iraklion at 17.1km (SE) Moúlia (GR: Μούλια) is a village in Kenouriou county, located three and a half kilometers away from Agia Varvara town and 32 km from Iraklion at an altitude of 640 m above sea level. Moulia is an old village as we come across a reference to it in a document dated in 1248, where the settlement is recorded as belonging to the archbishopric of Crete. Another reference is found in a legal agreement established in 1411. The name figures in all the Venetian censi of the 16th and 17th centuries, as well as in the Turkish and Egyptian censi. In 1881, it forms part of the municipality of Zaros with about 180 inhabitants, and again in 1900. As of 1920 it is a commune in its own right, and today with the lower village of Kato Moulia it counts over 550 inhabitants. The main church of the village, with wall paintings, is that of the patron saints, Saints Peter and Paul, and there is a village feast on the 29th June, in their honour. The lovely chapel of Zoodochos Pigis is also well worth a visit.
 Malevizi, Iraklion at 17.2km (E) Agios Myron, with 708 inhabitants, lies 18 km from the city of Iraklion to the south west. Its one of the most important villages of the area with interesting town planning and impressive samples of traditional architecture. Built between two hills it commands a panoramic view and the school's clock, its main characteristic, is visible from almost everywhere in the area of Malevizi.  Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The Upper Court is the first of the three courts in the West Wing of the Palace. Its south side is supported by a strong retaining wall separating it from the West Court. On the west side, the 17 circular recesses in the ground indicate the presence of an equal number of wooden columns which probably supported a covered colonnade. The court is crossed from north to south by a raised "Processional Causeway", which, like those of the other palaces, would have been used for sacred processions and other rituals. The Upper Court also functioned as a kind of balcony from which one could watch the events taking place in the West Court, which is just to the south and on a lower level. The two courts are linked by a majestic staircase starting in the southeast part of the Court. The buildings on the south side of the court were built much later, in Hellenistic times (323-67 BC), when the palaces had already beendestroyed. The most important of these contains a room with two columns, a central hearth and stone benches around the walls. It isbelieved to be a public building, probably a Prytaneion or Andreion.Early Christian tombs (330-600 AD) can be seen east of the "Processional Causeway" Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The impressive staircase starting in the west Court led to the monumental Propylaea, the principal and most impressive entrance to the New Palace (1700-M50 BC). The portico consists of a central column - only the base is preserved today - flanked by pilasters. There followed a solid wall with a double opening and a colonnade of three columns. The floors of the Propylaea complex were paved with gypsum slabs which gave it a sumptuous appearance. The colonnade opens onto a large open-air light-well through which rainwater drained away. There are two accesses from the Propylaea to different parts of the Palace. The first access, in the hall with the colonnade, led via a staircase and corridors to the Peristyle and thence to the "Royal Apartments". The second, in the SE corner of the light-well, led to an inner staircase which ended in the Antechamber of the Magazines and the Central Court of the Palace. Image Library
North Wing Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The North Wing is one of the most important wings of the Palace, as it is believed to have housed the "Royal Apartments". lt also contained sets of rooms, inner courtyards, corridors and staircases leading to the upper floor. The splendid gateway on the north side of the Central Court led to the complex of the "Royal Apartments". It is framed by two magnificent wooden half-columns, now reconstructed. On either side of the gateway are two niches decorated with wall paintings, in which the gate guards may have stood. Behind the gateway is a wide corridor with a drainage duct, which led to an inner courtyard, which in turn led to the "Royal Apartments" complex. The term "Royal Apartments" was established by the excavators, who followed the terminology applied by Evans to similar areas at Knossos. They are undoubtedly official apartments with particular architectural features, such as open balconies and colonnades, polythyra (pier-and-door partitions), lightwells and "Lustral Basins". The gypsum slab flooring and colourful wall paintings gave these apartments a particularly luxurious appearance.  Image Library
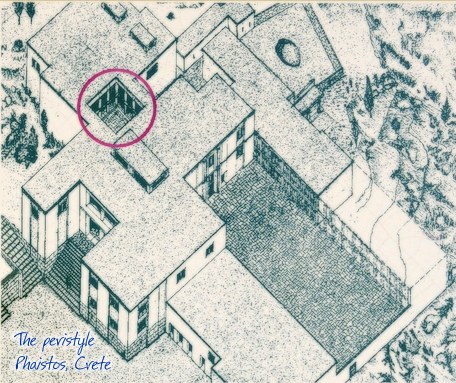
Peristyle Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The open peristyle court was one of the most elegant inner courtyards of the New Palace. It consisted of an impressive peristyle with four columns on each side supporting the corresponding colonnades, while the central area remained open. The same construction appears to have continued on the upper floor, with a second row of columns. The peristyle court was a focal point of the Palace with access routes leading from here to the "Royal Apartments", the Propylaea and the Central Court. The ruins visible on a lower level in the centre of the peristyle belong to a house of the Prepalatial settlement (3200-1900 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The northernmost of the "Royal Apartments" has been identified as the King's Megaron and bears a striking resemblance to the corresponding "King's Megaron" at the Palace of Knossos. It consists of a spacious central hall with impressive polythyra (pier - and - door partitions) on the north and east sides. The east polythyron communicates with a second room with two columns, which opens onto a large light-well to the east. The gypsum slab flooring with red plaster filling, the interstices, gave the whole complex a particularly sumptuous air. The north side of both rooms opens onto a spacious colonnade with columns set far apart, offering a magnificent view of Mount Psiloritis and the sacred Kamares Cave. A long corridor at the back of the polythyron room leads to the impressive "Lustra1 Basin" of the Megaron. The whole apartment was decorated with colourful wall paintings depicting linear and plant motifs. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 17.2km (S) The southernmost of the "Royal Apartments" ofPhaistos has been identified as the Queen'sMegaron. It consists of a beautiful, spacioushall with a double colonnade opening ontoa light-well. The floors are paved with gypsum slabswith red plaster filling the interstices. Gypsumwas also widely used for the benches runningaround the walls of the Megaron and the facingof the lower part of the walls. The upper walls aredecorated with frescoes depicting plant motifs. Twobeautiful rhyta (libation vessels) were found here: one is decorated with the cult symbols of thedouble axe and sacral knot, while the other bears areed pattern. The two staircases to west and north led to the upper floorof the Megaron and the peristyle, where one of the mainentrances to the "Royal Apartments" was located. Image Library
|
|||
|
| |||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S