interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
254
- Showing :
241 - 254
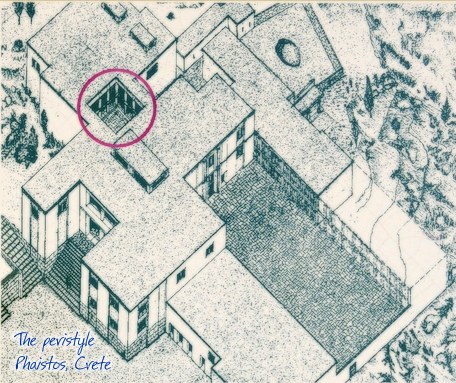
Peristyle Phaistos Palace at 47.7km (SW) The open peristyle court was one of the most elegant inner courtyards of the New Palace. It consisted of an impressive peristyle with four columns on each side supporting the corresponding colonnades, while the central area remained open. The same construction appears to have continued on the upper floor, with a second row of columns. The peristyle court was a focal point of the Palace with access routes leading from here to the "Royal Apartments", the Propylaea and the Central Court. The ruins visible on a lower level in the centre of the peristyle belong to a house of the Prepalatial settlement (3200-1900 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 47.7km (SW) The northernmost of the "Royal Apartments" has been identified as the King's Megaron and bears a striking resemblance to the corresponding "King's Megaron" at the Palace of Knossos. It consists of a spacious central hall with impressive polythyra (pier - and - door partitions) on the north and east sides. The east polythyron communicates with a second room with two columns, which opens onto a large light-well to the east. The gypsum slab flooring with red plaster filling, the interstices, gave the whole complex a particularly sumptuous air. The north side of both rooms opens onto a spacious colonnade with columns set far apart, offering a magnificent view of Mount Psiloritis and the sacred Kamares Cave. A long corridor at the back of the polythyron room leads to the impressive "Lustra1 Basin" of the Megaron. The whole apartment was decorated with colourful wall paintings depicting linear and plant motifs. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 47.7km (SW) The southernmost of the "Royal Apartments" ofPhaistos has been identified as the Queen'sMegaron. It consists of a beautiful, spacioushall with a double colonnade opening ontoa light-well. The floors are paved with gypsum slabswith red plaster filling the interstices. Gypsumwas also widely used for the benches runningaround the walls of the Megaron and the facingof the lower part of the walls. The upper walls aredecorated with frescoes depicting plant motifs. Twobeautiful rhyta (libation vessels) were found here: one is decorated with the cult symbols of thedouble axe and sacral knot, while the other bears areed pattern. The two staircases to west and north led to the upper floorof the Megaron and the peristyle, where one of the mainentrances to the "Royal Apartments" was located. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 47.7km (SW) The east part of the North Wing forms the workshop area of the Palace. It consists of the East Court and a complex of small rooms which are believed to be the workshops of the New Palace (1700-1450 BC). Approximately in the centre of the court are the ruins of a horseshoe-shaped kiln. The elongated rectangular building with 6 rooms on the west side of the court appears to have been used for the workshops of the kiln craftsmen. The square room on the north side of the court was the gatehouse of the northeast entrance to the Palace. It has gypsum slab flooring and benches around the walls. Behind it is a long corridor leading to the inner courtyard of the North Wing and thence to the "Royal Apartments" Image Library
 Palace and Archaeological Site at 47.8km (SW) The archaeological site, the palace, the findings - The Festos Disc. According to mythology, Phaistos (or Festos) was the seat of king Radamanthis, brother of king Minos. It was also the city that gave birth to the great wise man and soothsayer Epimenidis, one of the seven wise men of the ancient world.Excavations by archaeologists have unearthed ruins of the Neolithic times (3.000 B.C.).
Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 47.8km (SW) The large paved West Court, in front of the facade and the central entrance to the Palace complex, dates from the time of the Old Palace (1900 - 1700 BC) and played an important part in the lives of its inhabitants. On the north it is bounded by a high which also supports the Upper Court, which is on a higher level. At the foot of the wall are eight wide steps which formed the seats of what may be called a theatral area. As with the corresponding "Theatre" of Knossos, from here spectators would have watched the religious events and festivals taking place in the court. The West Court is crossed by a raised "Processional Causeway" similar to that of the Upper Court, which continues up the steps of the Theatral Area. During the time of New Palate the West Court was widened and raised to a higher level, so only 4 of its 8 steps remained visible. After the reduction of the Theatral Area, the great staircase must have been used as an additional theatral area for the events and ceremonies held in the West Court.  Phaistos Palace at 47.8km (SW) The south end of the West Court is occupied by four large stone-built structures known as "Kouloures" (rings) ,belonging to the Old Palace complex. The workmen on Evans' excavation gave them their name when they were first discovered at Knossos. Similar pits were also later discovered at the Palace of Malia. Their exact use is unknoun, although today they are generally regarded as depositories for offerings from the Palace shrines, or granaries. In front of the Phaistos "Kouloures" passes a "Processional Causeway" which starts in the West Court. One of the "Kouloures" is cut across by a cobbled road built in later years. The well next to them belongs to the Hellenistic period (323 - 67 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 47.8km (SW) The main facade of both the Old and the New Palace looked onto the West Court, off which the official entrances to the Palace opened. The facade which can be seen on a lower level belongs to the Old Palace(1900- 1700 BC). It is indented according to the rules of Minoan architecture. The lower part of the walls is constructed of massive limestone blocks (orthostats). The entrance is set into a recess in the SW corner of the court. lt consisted of a monumental porch with a large central column from which a splendid corridor, paved with gypsum slabs, led to the Central Court. This old entrance is now interrupted by the buildings of the New Palace. Higher up and 7 metres further back is the facade of the New Palace (1700-1450 BC). It is constructed of large ashlars and also has deep indentations and protrusions. There are two entrances leading to the interior of the Palace. The main entrance is on the north and consists of a monumental staircase leading to the Propylaea. The other is deeply recesed and leads via a wide corridor to the Oentral Court, crossing the West Wing of the Palace  by Richard Ellis at 47.8km (W) This is my log of the E4 long distance walk along the spine of Crete from East to West - it is intended to be a useful resource for others who are contemplating a similar walk along the E4 in Crete; it is not intended in any way to be a complete route guide.
 Found at Phaistos Palace at 47.9km (SW) The disc of Phaistos is the most important example of hieroglyphic inscription from Crete and was discovered around 1903-05 in a small room near the depositories of the "archive chamber", in the north - east apartments of the palace, together with a Linear A tablet and pottery dated to the beginning of the Neo-palatial period (1700- 1600 B.C.). The disc of Phaistos can be seen at the Archaeological Museum of Heraklion. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 48.1km (SW) The church of Agios Georgios (St. George GR: Αγιος Γεώργιος) Phalandras stands a little to the south from the Palace of Phaistos on the road to Agios Ioannis village. The church was the monastery church of the Orthodox male monastery of the same name, dated to the early Venetian period (16th century), which operated normally until its dissolution in 1821. The ruins of the fortified building complex around the church were still visible until the first decades of the 20th century. Image Library
Vassiliki - Archaeological Site Pahia Ammos, Ierapetra at 48.4km (E) The ancient settlement of Vasilike is one of the first Minoan settlements with town-planning. It occupies the top and slopes of a low hill near the village Vasilike, in the vicinity of the Minoan settlement of Gournia. The first settlement dates back to the Early Minoan II period (2600-2300 B.C.) and owed its development not only to the strategic position, controlling the Isthmus of Hierapetra, but also to the neighbouring fertile plains. The central building of the settlement was destroyed by fire in around 2300 B.C.  Archaeological Site in Messara, S-W Iraklion at 49.2km (W) The "Royal Villa" at Ayia Triada which is situated very close to Phaistos, was built in about 1550 BC. i.e. just before the new palace at Phaistos, and was destroyed by fire in l450 BC, like all other important Minoan centres. It succeeded the first palace at Phaistos as the economic and administrative centre of the regions depriving the new palace there of this role, and appears to have had connections with Knossos. The two wings, with an open-air space between them, consisted of groups of interconnecting rooms (polythyra), storerooms and stairways. On the site of the ruins, a Mycenaean megaron, the so-called "Agora" and an open - air shrine were subsequently built. In the villa's disaster layer from the fire in 1450 BC, excavation revealed a valuable group of exceptional works of art, precious materials, records in Minoan script and seals. The famous black serpentine vessels, the "Harvesters' Vase", the "Boxers' Vase" and the "Chieftain ‘ s Cup", the wall paintings depicting the natural landscape, the sarcophagus, the bronze and clay figurines of worshipers and the copper ingots from the Treasury are among the most noteworthy findings.  Messara, Iraklion South at 49.8km (SW) Its 1000 years history comes to life for the visitor, who has the chance to admire its monuments, and old houses, perfectly preserved through the centuries. In the village square , you can sit and enjoy your coffee in the traditional coffee shop, while children can play in the playground next to the school. You can also visit the church of Agios Ioannis in the same square. There are quite few rooms for rent in the village and tavernas serving traditional Cretan dishes.
|
||||
|
| ||||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S