interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
190
- Showing :
101 - 120
 Knossos Palace at 32.1km (S) North of the South Propylaeum, at a lower level there is the start of the corridor that joins eighteen long and narrow storerooms, covering an area of 1300 sq.m. In the floor of both the storerooms and corridor, there are ninety three rectangular cists, the so called "Kasellas". From the finds it appears they were used for keeping safe precious equipment and vases. There are also even larger cists in the corridor, internally lined, perhaps to hold liquids. The pithoi (large storage jars) of the "West Magazines" bear witness to the wealth of the palace. The remains of some 150 pithoi were found, although there is room for about 400. Their contents are unknown, although they could have oil, wine, pulses, etc. At different points of the magazine, clay tablets came to light in the Linear B script with records of an economic character. At the north end of the corridor, a large number of older clay seal impressions and clay tablets in the Cretan Hieroglyphic script were discovered. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 32.1km (S) To the south of the Throne Room and the stairs, lies the area that has been identified as a shrine, called by Evans the "Tripartite Shrine" (Evans's restoration drawing). Its facade had columns and was divided into three parts, the central element being the highest. There is a depiction of a comparable shrine on a wall painting now on display in Heraklion Museum. Inside the shrine were found clay tablets in the Linear B script and clay seal impressions which were possibly connected with the archive of a shrine. The remaining areas behind the "Tripartite Shrine" are thought to have been connected with the sanctuaries of the palace. At the back, two small dark rooms with pillars are known as the "Pillar Crypts". The depresions in their floor are said to indicate that these rooms were used for libations. In another room, two large, rectangular, stone-built repositories were found, sunk into the floor. They were full of clay vases and valuable objects, amongst which were the statuettes representing the "Shake Goddess". The repositories have been interpreted as the "Temlple Repositories". The stairs on the right lead from the Central court to the upper floor of the West wing. This is largely reconstructed by Evans. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 32.1km (S) The great staircase and the upper floor to which it leads are largely Evans’ creation. Evans thought that it had a function rather like the first floor of Italian Palazzi of the Renaissance, which was called Piano Nobile. In this instance, he considered that the important reception rooms of the palace would lie on the upper floor. Evans also thought that there existed a shrine, the "Tri-Columnar Shrine", and its Treasury. The basis for his restoration lies in the column and pillar bases and the ritual stone vases found collapsed onto the ground floor, like the alabaster one in the shape of a lioness head. The rectangular building next to the stairs was built a long time after the destruction of the palace. Evans interpreted it as a "Greek Temple" based on finds of the historic period.
Image Library
 Excavator of Knossos at 32.1km (S) British archaeologist whose name is inextricably bound up with excavations and restoration work at the palace of Knossos. Born as the son of numismatist John Evans, he studied at Oxford and briefly in Göttingen. From 1875 to 1882 he travelled through the Balkans as a correspondent of the Manchester Guardian. In 1884 he was appointed curator at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, which post he held until 1908. One year later he became a university don. In 1894 Schliemman's excavations at Troy, Mycenae and Tiryns prompted Evans to visit Crete for the first time, in search of Bronze Age script. The following year he published his first book on Cretan pictographics and pre-Phoenician writing. He set about systematic excavation work after the island was liberated from the Turks (in 1898), having already located the wider area in which to dig. At the same time he toured the length and breadth of Crete. Evans worked at Knossos for no less than 35 years, bringing the palace and countless finds to light. The building's large surface area and shape led him to the conclusion that it had been the palace of King Minos. He thus gave the name 'Minoan' to the civilization he had uncovered, subdividing it into three major periods. In 1911 he was knighted for his excavation activity and extensive work. Alongside the excavations, Evans showed great zeal in restoring the palace and reconstructing the wall paintings that had come to light. For all the intense criticism this part of his work has often attracted, it still stands as a first approach to what is now known as the Minoan palace. The ensuing publications of material added many pieces to the puzzle of Minoan civilization and remain useful research tools to this day. In the course of his last visit to Crete, Evans was given the Freedom of the City of Heraklion. Image Library
 Discovered Knossos at 32.1km (S) Born in 1843 as the youngest son of Andreas Kalokairinos. Having completed secondary education on the island of Syros, he matriculated at the University of Athens School of Laws and attended for one year, but was forced to abandon his studies after his father fell seriously ill and died. Thereafter his interest turned to his father's estates, which he initially managed together with his brother Lysimachos. Kalokairinos later went into soap manufacture, winning awards at world exhibitions. Unfortunately, however, his business enterprises were not destined to be successful to the end; in 1895, having taken out numerous loans at exorbitant interest rates and mortgaged all his estates, he was forced to declare bankruptcy and was thus deprived of the right to engage in commerce. In 1903 he decided to resume his legal studies at university, and was later awarded a a degree. In 1878 his passion for archaeology and classical studies led him to attempt the first systematic excavations at Knossos, which brought the first finds from the Minoan palace to light. These comprised the Kalokairinos private collection, held at the site where the Kalokairinos Mansion (the present-day Historical Museum of Crete) was later built. The finds were destroyed when the first mansion was burnt to the ground during the 1898 riots. In 1869 Minos Kalokairinos married Skevo Kyriazi, with whom he had five children.  Knossos Palace at 32.1km (S) This area, sited at the north-west edge of the palace, was called the "Theatre" by Evans because its shape reminded him of later theatres. It is a platform and rows of steps that form a right angle. At the base of the stairs is the end of a narrow elevated road that crosses a paved court. Evans believed that the court was used for ceremonies watched by the standing viewers. The elevated paved road continues in the opposite direction. It passes underneath the modern road to Heraklion, connecting the Palace with the Minoan town, which extended to the West and North. Evans named the road the "Royal Road". Along the length of the road are town houses with workshops on the ground floor and residential areas on the upper floor. Image Library
 Knossos at 32.3km (S) Villa Ariadne was built at Knossos, Crete, by Sir Arthur Evans soon after he discovered the Minoan palace, when the site was his own private property. The villa became home, in turn, to John Pendlebury, who used it as a base for his excavations at Knossos and his explorations of the island. After Pendlebury's death at the hands of invading German paratroopers, the Villa Ariadne was taken over by General Karl Kreipe, who was living there when he was kidnapped by Patrick Leigh Fermor and his team. Ariadne villa is surrounded by the only existing Greek Edwardian garden, a large oasis of Cretan and other flora and shrubs in specific formations. The garden has been fully studied by the British School of Archaeology with the participation of special architects and agronomists from Heraklion.  Ierapetra, Lassithi at 32.4km (S) A stately village built in settlements, 22 km away from Ierapetra, at an altitudeof 225 m, next to the Ierapetra-Vianos provincial road. A green landscape,overgrown with olive trees, with an unlimited view of the Libyan Sea, to thesurrounding areas Koleitos, Kakon Oros, to the beaches Vatos and Kallikovrechtis.An almost abandoned village, with old houses built of stone, with chiseled doorframes and coats of arms bearing the Christian cross and proving its old gloryand history.Giannis Dimitromanolakis, an author from Gdohia, writes:“Gdohia sprouted right opposite the beach of the Libyan Sea. Nothing wouldhave been better for the pirates, who, like diabolical ghosts, emerged into thenight to kill and prey. The village’s history is dipped in blood, as it often sufferedfrom the raids of the pirates from the Barbary Coast. It took the name Gdohiafrom the catastrophes, from the verb “gdyno”, to skin, to set fire, to devastate.”Gdohia’s course in time has evidence of struggles, sacrifices and holocausts toshow. It was not only exposed to the pirates but it was situated on the naturalsouth passage going from the Viannos area to the Ierapetra area. This meantthat the hordes of barbarous conquerors burnt and devastated it, along withthe other Symiana villages, as they are called, in the West Ierapetra.Gdohia’s settlements are built leaving a distance between each other: KatoGdohia or Pitropiana, taking their name from the Epitropakis family livingthere, Pefkiana or Grysboliana, from the Grysbolakis family, Dimitromanolianafrom the Dimitromanolakis family, Daskaliana from the Daskalakis family,Papadiana from the Papadakis family. Great stonecutters, stoneworkers,famous for their art, Gdohia’s residents built the mansions of the whole areaand the famous bridge of Myrtos using stones from the quarries of Kolleitos.The miraculous church of Panagia (Our Lady) Evaggelistria of Gdohia, a workof art and a great ecclesiastical monument is also built by Gdohia’s residents.Gdohia village, once the seat of a Community, today a Local Department ofthe Municipality of Ierapetra, presents an exceptional sight-seeing interest. Itprovides natural landscapes, beautiful beaches, picturesque little churches onthe hills, a spacious square with palm trees, seats and a war memorial forthe fallen fighters of the liberation wars. In the 1881 census, 296 residents areregistered and 73 in 2001. Gdohia’s permanent residents, along with someforeigners’ families who have bought and renovated old houses, struggle forthe village’s development which gradually acquires the necessary infrastructures.A village with rich history and civilization, with vast olive groves, a nicemild climate, both during summer and winter, it hopes to come back to life.The old mansions, half-wrecked and burned in the German Occupation, standas if they were sculptures, a painting with the deep blue Libyan Sea serving asa background, narrate the flourishing, the glory and the history of Gdohia andwait to be inhabited again.
 Archanes, Iraklion at 32.8km (W) A small traditional town (~4000 people) 15 km south of Iraklion on the foot of the sacred mountain Yiouhtas. Renowned for its excellent wine (from the varieties: vilana, kotsifali and madilari) and the archaeolocical sites and caves. In 1912, Xanthoudides noted the importance of Archanes, but Sir Arthur Evans was the first to characterize the site as palatial, declaring that Archanes was likely a Summer Palace for the Knossos kings. Spyridon Marinatos and N. Platon excavated minor areas in the region, but nothing supported Evans' theory. In 1964, J. Sakellarakis dug trial trenches at the Tourkoyeitonia site and uncovered the first evidence of a palace site. Since 1966, Archanes has been excavated by the Greek Archaeaological Society under the supervision of John Sakellarakis and Efi Sapouna-Sakellarakis. The small town of Epano Archanes, one of the most famous places of the Cretan land, with its colorful courtyards, teaches culture, taste, tradition, colors, aromas and life itself. The silvery grays of the olive groves, the red, pink, salmon and tiled walls, the blue and green shutters, the colorful bougainvillea boldly climbing the walls of the houses, the manicured flower beds, but also the elaborate, colorful signs in coffee shops and grocery stores. All this makes Archanes the most colorful village of Crete, but also of Greece. The town is full of atmospheric neighborhoods with well-maintained houses, painted in cheerful colors. At each step the visitor learns more and more about it. That's why the locals have taken care of it: the Folklore Museum, the Archaeological Museum, the sculpture workshop, the Museum of Cretan History and Tradition just outside. Image Library
 Ierapetra, Lassithi at 32.8km (SE) It is a small village, 7 km to the north of Ierapetra, at an altitude of 212 m. According to tradition, the village took its name from a large olive tree. It produced at least 10 sacks of olives and it provoked admiration by its size, and mostly by its height (Makrylia meaning tall olive tree). The village is old and traditional, with original Cretan style houses that have remained untouched over the time, in a beautiful and healthy environment, with a view of the overgrown with olive trees plain, with a rich history and hospitable residents.  Knossou Av. Iraklion at 32.8km (W) The General Hospital of Heraklion "Venizeleio & Pananio", named after the great statesman Eleftherios Venizelos, is one of the largest hospitals in Crete with 500 organic beds. It is located 4km away from Heraklion center on the road to Knossos, and occupies an area of 25,000 sq. meters. Venizeleio hospital provides high quality health services to citizens in a friendly and human environment. It was established in 1953 by a donation of Cretans of America and worked initially for Pulmonary Diseases. It was for many years the major hospital in East Crete. Telephone: (+30) 2813 408000 Website: www.venizeleio.gr/  Houdetsi, Iraklion at 33.1km (W) The Musical Workshop "Labyrinth" organizes seminars, concerts and various creative activities around modal traditional musics of the world. Labyrinth Musical Workshop was founded in 1982 by Ross Daly, with the goal of initiating young people, primarily, into a creative approach to traditional musical idioms from various parts of the world.  Archanes at 33.2km (W) Excavations at Phourni have brought to light 26 buildings, most of which had funerary use. The cemetery was used from 2400 B.C. until 1200 B.C. and each complex had more than one architectural phase. Most of the funerary buildings were used for many decades and contain successive burials. Excavations were begun in 1964 by Efi and John Sakellarakis and have been continued until today (1995) with short interruptions. Most of the buildings are preserved in good condition.  Archanes at 33.3km (W) An excellent specimen of a specialized building, one of the first structures erected during the period of the Cretan State. It was designed by the architect Salivero, one of Prince George's officials. The plans were completed in 1901 and the construction was accomplished thanks to donations of rich Archanians living in the U.S.A. The building is Pi-shaped in plan, has two storeys and a basement, it is built of stone and its roof is partially wooden and covered with tiles. It is a monumental but well balanced structure with many harmonic and elegant Neoclassical features. Since its construction, the building has been used as a school. During the German occupation it housed General Muller's division. Source: The Hellenic Ministry of Culture  Pahia Ammos, Ierapetra at 33.4km (SE) Gournia lies on a small hill, a few hundred metres from the sea in the Gulf of Mirabello, close to the north end of the Ierapetra isthmus ( 2 Km from Pachia Ammos village & 19 Km from Ag.Nikolaos). Gournia - the ancient name of which is not known - is the most characteristic of the excavated medium-size settlements, dated to the period of the peak of the Minoan culture (Late Minoan I period: 1550-1450 B.C.). It is called "Pompeii of Minoan Crete" because of the good state of preservation. It occupies a low hill, close to the sea, at the Isthmus of Ierapetra.  Archane, Iraklion at 33.4km (W) The Archaeological Museum of Archanes opened in 1993. It occupies an area of 570 square meters and it is located at the Tzami quarter in the center of the settlement. There, for the first time in Crete, the archaeological finds from a single site are exhibited. While the exterior spaces of the building were adapted to a tasteful ensemble, in resemblance with the impressive modesty of the environment and the traditional ochre and rosy colour tonations of Archanes. The interior was thus arranged as to accommodate the most modern mode of exhibition, especially attractive for the visitor.  Iraklion at 33.6km (W) The Port of Heraklion is the main and most modern gateway for the transport of passengers and commodities on the island of Crete. There are three main companies that connect Iraklion to mainland Greece, Minoan Lines, Superfast Ferries and ANEK. During the winter months there are daily trips from Athens to Iraklion. The trip takes approximately 6 - 9 hours by ferry boat. The ships depart Athens in the evening (10.30 p.m.) and arrive in Iraklion at 5:00 - 6:00 a.m. There is also a weekly trip to Thessaloniki. During the summer season all companies operate also an extra daily trip that departs in the morning from Athens and arrives at Iraklion port in the afternoon. Finally various other companies operate ships connecting Iraklion with other island in the Aegean (Rodos, Santorini etc.). Daily cruises are also offered to the island of Santorini. Image Library
 North - Central Crete at 34.1km (W) Iraklion (Heraklion or Herakleion GR: Ηράκλειον) is the largest urban centre in Crete, the capital of the region and the economic centre of the island. The first European civilisation, the Minoan civilisation, flourished on this land 5000 years ago. Currently the population of Iraklion is approximately 150.000 people. It is a very dynamic and cosmopolitan town, particularly during the summer period when thousands of visitors can be seen shopping in the market or visiting the museums and other places of interest. Today Heraklion is the top choice for tourist destinations in the Mediterranean. The city is also the commercial and scientific centre of the island. During the last 20 years the city has made remarkable progress in the academic and technological fields...
Image Library
 Pachia Ammos at 34.1km (SE) The Institute for Aegean Prehistory Study Center for East Crete (or INSTAP-SCEC) is a unique facility for archaeological research, especially in the area of Aegean Prehistory. The Center is committed to stimulating and facilitating publication in the broader field of Cretan studies, with a focus on archaeology and ethnology.
 Archanes at 34.2km (W) Anemóspilia (GR: Aνεμόσπηλια). Anemospilia is an archeological site at the northern foot of Mount Yuchtas, in the prefecture of Heraklion in Crete. A rectangular building has been found which dates from the Minoan era and was destroyed by an earthquake in the 17th century BC. The building with three narrow chambers, each opening into a long corridor to the north, which extends along the whole width of the building. The area is enclosed with a stone wall and the whole structure has been interpreted as a shrine; in the central room was found a "xoanon" (statue) of the deity worshiped here. In the west room, where the altar stood, was uncovered, according to the excavator, the first human sacrifice to have ever taken place in Minoan times. (although this view has been challenged). The building at Anemospelia was used for only half a century, as it was suddenly destroyed by an earthquake in the middle of the 17th century B.C. The site was excavated in the summer of 1979 by John Sakellarakis.   Aerial view 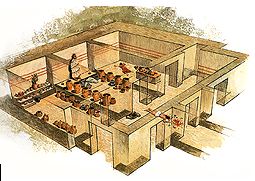 Shrine model Links: Minoan Religion (Foundation of the Hellenic World) |
||
|
| ||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S


