interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
186
- Showing :
101 - 120
 Nirou Chani, North - East Iraklion at 40.6km (NW) A Luxurious, two-storey house, built of large ashlar. The walls were strengthened by timber-frames and covered with a thick layer of plaster and marble slabs. The building has a paved courtyard, a shrine, storerooms for agricultural products, a staircase, and rooms with benches. It has been interpreted as a High Priest's house, due to the numerous ceremonial vessels it contained. The house was probably built in the 16th century. C. (MM III period) and, after its destruction by fire in the 15th century BC (LM IB period), was finally abandoned. The "Minoan Megaron" at Nirou was excavated in 1918 by St. Xanthoudides. In 1960, under the supervision of the Ephor of Antiquities N. Platon, the site was fenced and the building restored. The monument is consolidated and cleared at intervals by the 23rd Ephorate. Visiting Hours: Daily: 8:30-15:00, Monday: closed Entrance Fee:Free Admission  Archanes at 41km (W) The Minoan villa at Vathypetro was most likely the residence of a local ruler. Its architecture is comparable to that of a "Little Palace": it has a central and west court, a small tripartite shrine, a three-columned portico, storerooms and workshops. It seems that the construction of the building was never completed. Interesting elements of its architecture are the installations of a wine-press in the south wing and an oil-press in the courtyard.  Archanes, Iraklion at 41.1km (NW) A small traditional town (~4000 people) 15 km south of Iraklion on the foot of the sacred mountain Yiouhtas. Renowned for its excellent wine (from the varieties: vilana, kotsifali and madilari) and the archaeolocical sites and caves. In 1912, Xanthoudides noted the importance of Archanes, but Sir Arthur Evans was the first to characterize the site as palatial, declaring that Archanes was likely a Summer Palace for the Knossos kings. Spyridon Marinatos and N. Platon excavated minor areas in the region, but nothing supported Evans' theory. In 1964, J. Sakellarakis dug trial trenches at the Tourkoyeitonia site and uncovered the first evidence of a palace site. Since 1966, Archanes has been excavated by the Greek Archaeaological Society under the supervision of John Sakellarakis and Efi Sapouna-Sakellarakis. The small town of Epano Archanes, one of the most famous places of the Cretan land, with its colorful courtyards, teaches culture, taste, tradition, colors, aromas and life itself. The silvery grays of the olive groves, the red, pink, salmon and tiled walls, the blue and green shutters, the colorful bougainvillea boldly climbing the walls of the houses, the manicured flower beds, but also the elaborate, colorful signs in coffee shops and grocery stores. All this makes Archanes the most colorful village of Crete, but also of Greece. The town is full of atmospheric neighborhoods with well-maintained houses, painted in cheerful colors. At each step the visitor learns more and more about it. That's why the locals have taken care of it: the Folklore Museum, the Archaeological Museum, the sculpture workshop, the Museum of Cretan History and Tradition just outside. Image Library
 Archane, Iraklion at 41.5km (NW) The Archaeological Museum of Archanes opened in 1993. It occupies an area of 570 square meters and it is located at the Tzami quarter in the center of the settlement. There, for the first time in Crete, the archaeological finds from a single site are exhibited. While the exterior spaces of the building were adapted to a tasteful ensemble, in resemblance with the impressive modesty of the environment and the traditional ochre and rosy colour tonations of Archanes. The interior was thus arranged as to accommodate the most modern mode of exhibition, especially attractive for the visitor.  Archanes at 41.6km (NW) An excellent specimen of a specialized building, one of the first structures erected during the period of the Cretan State. It was designed by the architect Salivero, one of Prince George's officials. The plans were completed in 1901 and the construction was accomplished thanks to donations of rich Archanians living in the U.S.A. The building is Pi-shaped in plan, has two storeys and a basement, it is built of stone and its roof is partially wooden and covered with tiles. It is a monumental but well balanced structure with many harmonic and elegant Neoclassical features. Since its construction, the building has been used as a school. During the German occupation it housed General Muller's division. Source: The Hellenic Ministry of Culture  Archanes at 41.9km (NW) Excavations at Phourni have brought to light 26 buildings, most of which had funerary use. The cemetery was used from 2400 B.C. until 1200 B.C. and each complex had more than one architectural phase. Most of the funerary buildings were used for many decades and contain successive burials. Excavations were begun in 1964 by Efi and John Sakellarakis and have been continued until today (1995) with short interruptions. Most of the buildings are preserved in good condition. 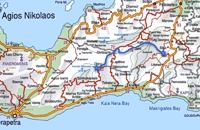 Richard Ellis walk: Day 3 at 43.5km (E) June 3rd - ...The short, direct, one marked with E4 signs ends in an olive grove with no way out ! You keep climbing on the basis that you will meet up with the Anavasi version of the route and then all of a sudden you find the dreaded stock fencing. I was lucky to find a way through (over) it, scramble up and over a ridge and see the easier, but longer, dirt road alternative on the other side of a full-flowing river. However, my choice of route seemed to be what the EOS expects you to do, as suddenly, and quite unexpectedly, there was another rare E4 sign on my side of the road on the way down to the river... Distance:24.7 km Time: 9 hrs. Mov av 4.3 km/hr Height overnight: 605m.(max 775 m.)  Archanes at 43.6km (NW) Anemóspilia (GR: Aνεμόσπηλια). Anemospilia is an archeological site at the northern foot of Mount Yuchtas, in the prefecture of Heraklion in Crete. A rectangular building has been found which dates from the Minoan era and was destroyed by an earthquake in the 17th century BC. The building with three narrow chambers, each opening into a long corridor to the north, which extends along the whole width of the building. The area is enclosed with a stone wall and the whole structure has been interpreted as a shrine; in the central room was found a "xoanon" (statue) of the deity worshiped here. In the west room, where the altar stood, was uncovered, according to the excavator, the first human sacrifice to have ever taken place in Minoan times. (although this view has been challenged). The building at Anemospelia was used for only half a century, as it was suddenly destroyed by an earthquake in the middle of the 17th century B.C. The site was excavated in the summer of 1979 by John Sakellarakis.   Aerial view 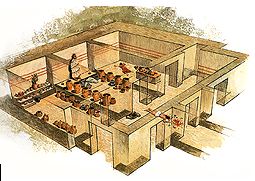 Shrine model Links: Minoan Religion (Foundation of the Hellenic World)  Sitia, East Lassithi at 44.1km (E) The Monastery of Kapsa is located 40 km from the town of Sitia at the exit of the Pervolakia Gorge built against the steep rocks overlooking the Libyan sea. The exact time of the foundation of the monastery is still unknown, while some believe that it was in the 15th century. Until 1841 there were only a small chapel dedicated to the Saint John the Baptist and a few cells. Image Library
 Iraklion at 44.2km (NW) This 2 km long sandy beach was for years and still is the favorite beach of the people of Heraklion town. It is named after the river "Karteros" which outflows at the west end of it near the airport. The water is clean, the seabed is sandy with smoothly shelving and swimming is safe. The access is free in most parts except for some areas that are reserved for military personnel and the municipal beach "Akti" where visitors should pay an entrance fee in order to use the facilities. At the east end there are some very good taverns offering fresh fish among their specialties and are very popular with locals and tourists alike.
Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.4km (S) The south-east house belongs to the New Palace period (1700-1450 B.C.). It was well built and decorated with wall-paintings of lillies. It had a pier-and-door partition, a pillar room and storage rooms. A little behind it are other houses of the Old Palace period (1900-1700 B.C.) such as the house of the "Sacrificed Oxen", named after the remains of a sacrifice found there (horns of a bull and a tripod table of offerings) and the "House of the Fallen Blocks", after the blocks that had fallen from the facade of the palace due to an earthquake. Next to "South-East House" there are houses of the Old Palace period (1900-1700 B.C.), such as that of the "Monolithic Pillars" in front of the steps. Under the small roof is a Minoan, possibly smelting kiln.  Palace and Archaeological site at 44.5km (NW) The famous Palace of king Minos and the centre of the Minoan civilisation 5km south of Iraklion. The Great Palace covered an area of 20.000 sq. meters and had 1.400 rooms. Every section of the Palace had a specific use. In the west side of the Palace were the chambers of the ceremonies, of the administration and of the public storehouse...
Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The Corridor of the Procession is named from the wall painting decorating its east wall and depicting a procession of musicians and other people holding gifts. The floor was very fine. The "Corridor of the Procession", according to Evans, initially led to the "South Propylaeum" and continued on to the Central Court. Today a causeway made of wood, with handrail, stands in its place, so the visitors can follow the same route. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The "South Propylaeum", as we see it today, is a result of the restoration of Evans who put up a copy of the "Cup-Bearer" fresco here. The wall painting depicted a man holding a libation vase (rhyton). Its theme is connected with the "Procession Fresco" which, according to Evans, reached here, the "South Propylaeum". The pithoi (large storage jars) on the east side of the Propylaeum belong to the Postpalatial Period (1450-1100 B.C.), and indicate that the area was later used for storage.
Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The south part and south facade of the palace is very eroded. Today one can only see foundations on tiered levels. At the bottom, a tower-like projection is all that remains of the south entrance to the Palace. An asceding corridor led to the Central Court. The section of the corridor closest to the Central Court was reconstructed by Evans who put here a copy of a relief wall painting, of which only few fragments were found. On these fragments, it was possible to make out a figure wearing jewellery in the shape of lilies. The reconstruction we see here is uncertain. In Evans's opinion, it represented the "Priest-King". Other scholars think that it is a prince, whilst others believe it depicts a female figure. Anyway the original fresco which is known as the "Prince of Lilies" is one of the masterpieces in the collection of the Heraklion Museum. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) North of the South Propylaeum, at a lower level there is the start of the corridor that joins eighteen long and narrow storerooms, covering an area of 1300 sq.m. In the floor of both the storerooms and corridor, there are ninety three rectangular cists, the so called "Kasellas". From the finds it appears they were used for keeping safe precious equipment and vases. There are also even larger cists in the corridor, internally lined, perhaps to hold liquids. The pithoi (large storage jars) of the "West Magazines" bear witness to the wealth of the palace. The remains of some 150 pithoi were found, although there is room for about 400. Their contents are unknown, although they could have oil, wine, pulses, etc. At different points of the magazine, clay tablets came to light in the Linear B script with records of an economic character. At the north end of the corridor, a large number of older clay seal impressions and clay tablets in the Cretan Hieroglyphic script were discovered. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The antechamber of a complex of rooms that Evans named the "Throne Room". Its name comes from the stone seat found in the room behind the antechamber, and between them were discovered traces of a burnt wooden construction. Today, a wooden seat has been placed here which is a copy of the stone one in the neighbouring chamber. After the antechamber is the central room of the complex. Right and left of the stone seat are yet more stone benches. Pieces of fresco depicting plants and griffins, mythical beasts with a lion's body and bird's head were found in the same room. The restored fresco is in Heraklion Museum. Evans put a copy in its place. Stone vases for oil, often connected with rituals, were found on the floor. The stone basin you see was actually found in a neighbouring corridor and placed here. To the left, a low partition wall with a purification ceremonies and therefore called them "Lustral Basins". The central room connects at the back with a series of small, dark rooms which were lit by lamps, as the finds illustrate. The function of the complex is difficult to determine. Evans believed that the rooms were used for ceremonies with the main figure being the king of Knossos in his religious capacity. However, it seems unlikely to have been a Throne Room in the modern sense of the word. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) To the south of the Throne Room and the stairs, lies the area that has been identified as a shrine, called by Evans the "Tripartite Shrine" (Evans's restoration drawing). Its facade had columns and was divided into three parts, the central element being the highest. There is a depiction of a comparable shrine on a wall painting now on display in Heraklion Museum. Inside the shrine were found clay tablets in the Linear B script and clay seal impressions which were possibly connected with the archive of a shrine. The remaining areas behind the "Tripartite Shrine" are thought to have been connected with the sanctuaries of the palace. At the back, two small dark rooms with pillars are known as the "Pillar Crypts". The depresions in their floor are said to indicate that these rooms were used for libations. In another room, two large, rectangular, stone-built repositories were found, sunk into the floor. They were full of clay vases and valuable objects, amongst which were the statuettes representing the "Shake Goddess". The repositories have been interpreted as the "Temlple Repositories". The stairs on the right lead from the Central court to the upper floor of the West wing. This is largely reconstructed by Evans. Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The great staircase and the upper floor to which it leads are largely Evans’ creation. Evans thought that it had a function rather like the first floor of Italian Palazzi of the Renaissance, which was called Piano Nobile. In this instance, he considered that the important reception rooms of the palace would lie on the upper floor. Evans also thought that there existed a shrine, the "Tri-Columnar Shrine", and its Treasury. The basis for his restoration lies in the column and pillar bases and the ritual stone vases found collapsed onto the ground floor, like the alabaster one in the shape of a lioness head. The rectangular building next to the stairs was built a long time after the destruction of the palace. Evans interpreted it as a "Greek Temple" based on finds of the historic period.
Image Library
 Knossos Palace at 44.5km (S) The Central Court (dimensions ca. 50m x 25 m.) is an architectural element common to all Minoan palaces. The Court connects the different wings with one another. There was also direct access from outside the Palace. Part of the paving, which once covered the whole court, is preserved in the northwest and southwest corners, whilst near the "Throne Room", parts of the drainage system can be made out which ensured the evacuation of rain water. It is thought that the area must have been for meetings and rituals of both a sacred and profane character The orientation of the Central Court was north-south with a clear view of the sacred Mount Giouhtas, where an important sanctuary was located. Image Library
|
||
|
| ||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S


