interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
: History & Archaeology
List Grid Map
Found
54
- Showing :
21 - 40
 Gortyn archaeological site at 31.4km (SE) This unique monument has been excavated in the last thirty years. It is located on the road between the Saint Titos Church and the village Mitropolis. It is the largest early Byzantine basilica in Crete and among the largest in whole Greece. In early Byzantine period it was the cathedral of the city. The first five-aisled basilica was erected here in the early 6th c., in the years of the Emperor Justinian and stood for about 70 years. The central aisle had a mosaic pavement decorated in geometric patterns and animals. It is believed that there were mosaics of stone and glass tesserae on the walls, too. The other aisle had pavements of limestone slabs. The columns were made of white and gray white marble. Of great importance is the pulpit, which resembles that of Saint Sophia in Constantinople. It was a high exedra on low columns and two stairs for ascent and decent. The choirs stood under the exedra. After the destruction of the first basilica in 620 AD, a new basilica was built over its ruins in the time of the Emperor Heraclios. This basilica, following the fortune of the whole city, was destroyed after the strong earthquake of 670 AD.
Image Library
 Gortyn at 31.6km (SE) The Temple of Apollo Pythios (Pythian Apollo) located in the center of the ancient Agora, was excavated in 1887 and was the largest temple and the religious center of ancient Gortyn until the introduction of Christianity and the founding of the basilica of St. Titus around 500 AD. The first building of the seventh century. BC was a four-sided enclosure with four wooden pillars in the center to support the roof. The exterior walls and stairs of the crepis were covered with archaic inscriptions. In the Hellenistic period a monumental anteroom was added while columns with inscriptions were placed between the pillars. Alterations and additions were made during the Roman period. Outside the temple was built a magnificent altar on a stepped base while in the west of the temple was built a small theatre. In the middle Byzantine period in the vicinity of the temple, which had been abandoned, were built houses and aqueducts. Many finds have been made in the temple among which the colossal statue of Apollo Pythios and many inscriptions with administrative and law content of the Archaic and Hellenistic period. Dates: 7th c BC; Hellenistic; 2nd c AD. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 31.6km (SE) The sanctuary of the Egyptian deities (1st-2nd centuries A.D.) is the only one, in the whole island, which is dedicated to the Egyptian gods Isis, Serapis and Anubis - Hermes although it is known that those gods are worshiped in other cities. The sanctuary consists of quadrilateral nave, arcade on the west, underground crypt in the south and a cistern outside east of nave. In the central alcove stood the statue of Serapis and the side statues of Isis and Hermes - Anubis. In the southern part of the temple was oblong space, underground crypt purification and a small cictern. The final construction phase of the temple dates to the 1st / 2nd century. AD, in accordance with dedicatory inscription. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 31.7km (SE) The Great Nymphaeum (Nymphaion GR: Νυμφαίον), located to the north of Praetorium, was a marble construction with a covered cistern and fountains. Statues of Nymphs stood in the niches. The area of the remains is closed to the public but visitors can see it from a distance.
Image Library
 Gortyn at 31.8km (SE) The Praetorium was the seat and residence of the proconsul of Crete. It is divided into two parts: the administrative section, in which the central building is the basilica, and the more "private" sector. The preserved ruins are dated to the 2nd century A.D. and seem to have been repaired in the 4th century A.D. This totally excavated building is the largest in the whole City of Gortyn. The earliest constructions have suffered successive alterations in a long period of eight centuries. New structures were erected on the ruins of the earlier sometimes incorporating parts of them. In the 1st c AD the Praetorium consisted of a peristyle court 1000 sq.m. and large halls to the north and west. This first Praetorium was destroyed by an earthquake in the time of the Emperor Trajan (early 2nd c AD). It was reconstructed and a large Thermai complex was built at its east side. Some years later a large temple dedicated to the Augusts was built further at the east part. To the west of the Thermai the juridical basilica continued to function under a judge’s responsibility according to the inscriptions found there, and statues of the emperors and other officers were still standing there. All these famous buildings were destroyed by the large earthquake in 365 AD. In 383 the consul Oecumenius Asclepiodotus Dositheus, agreeing with the capital of the empire, took care of the construction of the new Praetorium. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 32.1km (SE) It lies at the south eastern part of the city and it is considered to be largest of all theaters in Gortyna. Although it is not yet excavated, it is believed that it had a two storeyed stage and its cavea was supported by 56 arches. The statue of the seated philosopher that we see next to the exhibition hall of the archaeological site was found here.
Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 32.2km (SE) The Hippodrome was located in the south part of the city of Gortyn, and was surrounded by columns. The central section was 374 metres long and 60 metres wide. Our information on the site is insufficient for the reason that there was never a systematic survey, or even a small excavation. What we see today of this magnificent monument are only some parts of columns and capitals.
Image Library
 Tylissos at 32.6km (E) The houses of Tylissos were built during the LM I period (16th-15th century B.C.). Additions were made on House A in the LM II (15th-14th century B.C.) and on House C during the LM III period (14th century B.C.). The site was destroyed by fire in the 14th century B.C. and re - inhabited in historic times as is attested by ruins of later houses over the Minoan ones. Tylissos was excavated by Joseph Chatzidakis in 1902-1913. In 1954, in the course of restorations, parts of a paved court were revealed to the west, and a small stoa with five columns to the north of the Square of the Altar. The monuments were restored by the Archaeological Service (under the direction of Nicolaos Platon) in the period between 1954 and 1962. All three houses were again restored in 1990-1994. Source: The Hellenic Ministry of Culture  Rethymno south at 32.7km (W) Two small villages, Epano & Kato (Upper & Lower) Rodakino halfway from Plakias to Frangokastelo, overlooking the bay of Korakas. Rodakino is 42 kms from Rethimnon, 27 kms from Hora Sfakion and 13 kms from Fragokastello. Rodakino is surrounded by small beaches some of them accessible only by foot, were visitors can isolate themselves from any trace of civilization. There are some small hotels and rooms to rent available and a couple of tavernas. The road to Rodakino is asphalt paved and there is a bus service to Rodakino from Rethimnon twice a day. In the village the visitor can find a taxi station, and a gasoline station. A doctor is available for medical emergencies on the village of Plakias approximately 15 kms from Rodakino. Rodakino played its own part during the eons, in the fighting of the Cretans against all the invaders. The village was totally destroyed during the Venetian occupation, with only one resident escaping to Peloponnese in Greece . Years after the destruction he returned to the site of the village, and he rebuilt it. In Kourkoylo one of the quarters of the village the first rising of the flag of the revolution against the Turks was raised on May 24th 1821. During the second World War the kidnapped German general Craipe was sent away from the bay of Korakas to the Middle East. Image Library
 Kenourgiou, Iraklion at 34.3km (E) Agios Thomás (GR: Αγιος Θωμάς) lies at 530 m above sea level. It is 30 km away from Heraklion and has a panoramic view over the whole area to the SE of Aghia Varvara. Agios Thomas is a very old village and the first reference we have of it, is in a document of 1371, where it is quoted as a feudal property of Petrus de Medio, and again in a document dated 1380. Later, it figures in all the Venetian censi of the 16th and 17th centuries. In 1881, and in 1900, it figures as part of the Megali Vrisi municipality, with 344 inhabitants. From 1920, it figures in all the censi as a community with a continuously growing number of inhabitants. Nowadays there are over 800 inhabitants.  Sfakia, South Hania at 37.6km (W) Kalikratis is a small mountainous village at the foot of the White Mountains (Lefka Ori) at an altitude of 750m above sea level. It is a traditional village with many well preserved stone houses. A German army of two thousand soldiers, invaded the village during the October of 1943 , burned it down and executed twenty men and nine women who did not manage to leave on time. A little to the south of the village starts the gorge of the same name which is part of the European hiking footpath (E4) and after some 4km walking ends at the village of Patsianos.  Sfakia, South Hania at 40km (W) On the south coast of Crete, on a magnificent white sandy beach, stands one of the most beautiful Venetian fortresses, Fragokastello, built in 1371. It is located approximately 170 km from Iraklion, 70 km from Rethimnon, and 70 Km from Hania. Today, Fragokastello is a small, but developing, community, with nice beaches covered in sand dunes, and limited, but increasing, tourist facilities.The Villages Patsianos and Kalikratis, the castle, the history of the place and the fenomenon of Drossoulites...
 Lentas, South Iraklion at 40.3km (SE) The first habitation of the site dates from the Neolithic and Early Minoan period (3rd millenium B.C.). In the late Classical period (beginning of the 4th century B.C.) the Gortynians established the sanctuary of Asklepios at the harbour. During the tremendous earthquake of 46 B.C. the city was destroyed and subsequently rebuilt. In the Early Christian and Byzantine periods, a small settlement developed and the basilica was erected. The most important monuments of the site are: The Temple of Asklepios., the "Treasury"., the Fountain, a large, three-aisled basilica, an Early Minoan settlement (2600-2000 B.C.), the West Stoa, the North Stoa, the Nymphaion and two large, mud-brick cisterns. 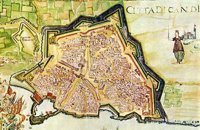 Iraklion at 42.9km (E) The fortified enclosure of the Venetian Chandakas of the 15th century, which is still preserved today, is one of the most significant monuments of its kind in the whole Mediterranean basin. Triangular in shape, with its base at the sea, the mighty enceinte has a perimeter of about 5.5 kilometres. The hallmark of the defensive layout are the bastions, linked by curtain walls decorated at many points by escutcheons and the lion of St. Mark, symbol of Venetian omnipotence. The gates in the enceinte, which served to link the town to the countryside, still stand as important architectural monuments. To this day, the walls that withstood the Ottoman siege in the mid-17th century mark out the boundary of the old town.  Archanes at 43km (E) Anemóspilia (GR: Aνεμόσπηλια). Anemospilia is an archeological site at the northern foot of Mount Yuchtas, in the prefecture of Heraklion in Crete. A rectangular building has been found which dates from the Minoan era and was destroyed by an earthquake in the 17th century BC. The building with three narrow chambers, each opening into a long corridor to the north, which extends along the whole width of the building. The area is enclosed with a stone wall and the whole structure has been interpreted as a shrine; in the central room was found a "xoanon" (statue) of the deity worshiped here. In the west room, where the altar stood, was uncovered, according to the excavator, the first human sacrifice to have ever taken place in Minoan times. (although this view has been challenged). The building at Anemospelia was used for only half a century, as it was suddenly destroyed by an earthquake in the middle of the 17th century B.C. The site was excavated in the summer of 1979 by John Sakellarakis.   Aerial view 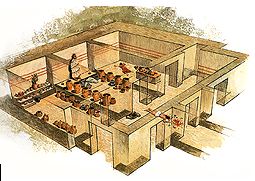 Shrine model Links: Minoan Religion (Foundation of the Hellenic World)  Iraklion Old Town at 43.3km (E) The Cathedral of St. Minas:The small church of St. Minas did not meet the religious needs of the constantly growing Christian community, so the demand arose for the erection of a new cathedral. The plot for the new church used to be a garden that belonged to a Turk from whom it was bought. The architect was Athanasios Moussis and in 1862 the foundation stone of one of the most magnificent and impressive Greek churches was laid. The outbreak of the Cretan revolution of 1866 demanded the stopping of the building work which will continue in 1883 in order to be completed in 1895, when the inauguration of the exquisite temple took place. The church is of the cruciform type with a dome based on a high spandrel, while internally there are also elements of a three aisle basilica. It has two bell towers, one in the northeastern corner and the other in the southeastern one. The right aisle is dedicated to Apostle Titos and the left one to St. Ten Martyrs of Crete. The inside of the church has gone through many changes with new additions. With plans of the architect Anastasios Orlandos the woodcut icon screen was replaced by another one made of marble, the same happened with the bishop's seat. The religious painting of the church was assigned to St. Kartakis who followed faithfully the principles and the models of the Byzantine icon painting. The hundredth anniversary from the inauguration of the Cathedral Church of St. Minas (1995) was celebrated with every solemnity that is suited in an equal occasion and more specifically to one of the most glorious and imposing Greek churches. Image Library
 Iraklion at 43.3km (E) The «General Provisioner» Antonio Priuli made it in 1666 and it is situated today behind the "Bodosakeio" Primary School (in the area of the Venetian Dermata Gate). He decorated it with round and square columns with Corinthian type capitals, while a triangular pediment crowns the whole construction. From both sides of the columns there are niches with their metopes elaborately decorated. In the middle of the fountain there is a Turkish inscription where there is a reference to the name of the Turkish pasha who managed to bring water again in the fountain.
 Iraklion town at 43.5km (E) The history and culture of Crete, from the first centuries of the Christian era to our present time. An exceptional museum featuring a collection of extremely precious objects, a must see for every visitor to Crete. The museum is housed in a two storey neoclassical building, which was constructed in 1903 on the site of an earlier mansion.
 Archanes at 43.6km (E) The Minoan villa at Vathypetro was most likely the residence of a local ruler. Its architecture is comparable to that of a "Little Palace": it has a central and west court, a small tripartite shrine, a three-columned portico, storerooms and workshops. It seems that the construction of the building was never completed. Interesting elements of its architecture are the installations of a wine-press in the south wing and an oil-press in the courtyard.  Iraklion Old Town at 43.6km (E) The "Morosini's fountain" or "Lions' fountain" that dominates the center of Eleftherios Venizelos square in Iraklion old town, is a landmark both for locals and visitors. A masterpiece of the Venetian era that would be the pride of any city in the world. It was made in 1628 AD, under the supervision of the General Provisioner Francesco Morosini, to satisfy Candia's (Candia was the Venetian name of Crete and its capital - Iraklion - as well) needs for water. For this purpose an aqueduct was constructed to bring the water from the sacred mountain Giouhtas. Image Library
|
||
|
| ||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S


