interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
171
- Showing :
81 - 100
 Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) Almost the whole south part of the West Wing was dedicated to the shrines of the New Palace. The main architectural types of shrine are the "Bench Shrine" and the "Lustral Basin". The first type consists of small, rectangular rooms with low benches running round the walls, perhaps to support cult objects and figurines of the deity. On some of them were found female figurines, ritual vessels and "Offering Tables" (small altars). On the walls of some rooms are incised sacred symbols, such as the double Axe and the star. The "lustral Basin" type consists of rooms which are set somewhat lower than the surrounding structures, with a few steps leading down into them. The were usually lined with slabs of gypsum, giving them a highly - finished appearance. Although it is doubtful that these structures contained water, it is thought that they were used for purification rituals. There is a third type of Minoan shrine in the S-E part of the shrine wing. Its is a room with central pillars (Square, stone - built columns) thought to be a cult area, similar to the "Pillar Crypts" of the Palace of Knossos, where the sacred pillar was worshiped by pouring libations.  Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The great Central Court is a basic architectural element of Minoan palaces and the core around which the different wings are set. It was the focus of the economic, social and religious activity of the palace, the setting for events which could be watched from the windows and balconies. The Central Court of the Palace of Phaistos was built in the time of the Old Palace (1900-1700 BC). It was also used in the New Palace with minor alterations to its orientation and dimensions. It is a rectangular paved, open area with colonnades running along both its long sides, with alternating pillars and columns which supported open colonnades.On the west side of the court, two adjoining rectangular rooms with benches, open on to the Central Court, may have been "sitting rooms" for the spectators watching the events taking place in the Central Court. In the east colonnade of the court, some stone-built benches next to a water cistern may have formed islands of rest and recreation. The stepped structure in the NW corner of the court may have been an altar for the ceremonies which were held here. The pithoi (large storage jars) in front of it were found in buildings founded in the site of the Great Court after the destruction of the Palace. Image Library
North Wing Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The North Wing is one of the most important wings of the Palace, as it is believed to have housed the "Royal Apartments". lt also contained sets of rooms, inner courtyards, corridors and staircases leading to the upper floor. The splendid gateway on the north side of the Central Court led to the complex of the "Royal Apartments". It is framed by two magnificent wooden half-columns, now reconstructed. On either side of the gateway are two niches decorated with wall paintings, in which the gate guards may have stood. Behind the gateway is a wide corridor with a drainage duct, which led to an inner courtyard, which in turn led to the "Royal Apartments" complex. The term "Royal Apartments" was established by the excavators, who followed the terminology applied by Evans to similar areas at Knossos. They are undoubtedly official apartments with particular architectural features, such as open balconies and colonnades, polythyra (pier-and-door partitions), lightwells and "Lustral Basins". The gypsum slab flooring and colourful wall paintings gave these apartments a particularly luxurious appearance.  Image Library
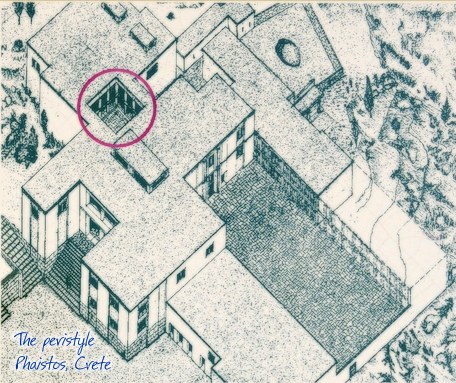
Peristyle Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The open peristyle court was one of the most elegant inner courtyards of the New Palace. It consisted of an impressive peristyle with four columns on each side supporting the corresponding colonnades, while the central area remained open. The same construction appears to have continued on the upper floor, with a second row of columns. The peristyle court was a focal point of the Palace with access routes leading from here to the "Royal Apartments", the Propylaea and the Central Court. The ruins visible on a lower level in the centre of the peristyle belong to a house of the Prepalatial settlement (3200-1900 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The northernmost of the "Royal Apartments" has been identified as the King's Megaron and bears a striking resemblance to the corresponding "King's Megaron" at the Palace of Knossos. It consists of a spacious central hall with impressive polythyra (pier - and - door partitions) on the north and east sides. The east polythyron communicates with a second room with two columns, which opens onto a large light-well to the east. The gypsum slab flooring with red plaster filling, the interstices, gave the whole complex a particularly sumptuous air. The north side of both rooms opens onto a spacious colonnade with columns set far apart, offering a magnificent view of Mount Psiloritis and the sacred Kamares Cave. A long corridor at the back of the polythyron room leads to the impressive "Lustra1 Basin" of the Megaron. The whole apartment was decorated with colourful wall paintings depicting linear and plant motifs. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The southernmost of the "Royal Apartments" ofPhaistos has been identified as the Queen'sMegaron. It consists of a beautiful, spacioushall with a double colonnade opening ontoa light-well. The floors are paved with gypsum slabswith red plaster filling the interstices. Gypsumwas also widely used for the benches runningaround the walls of the Megaron and the facingof the lower part of the walls. The upper walls aredecorated with frescoes depicting plant motifs. Twobeautiful rhyta (libation vessels) were found here: one is decorated with the cult symbols of thedouble axe and sacral knot, while the other bears areed pattern. The two staircases to west and north led to the upper floorof the Megaron and the peristyle, where one of the mainentrances to the "Royal Apartments" was located. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The complex of four rooms on the northeast edge of the Palace does not belong to the Old Palace, although it directly adjoins it. In the westernmost building is an elongated rectangular room with partitions of vertical clay slabs. Similar "cists" in the Palaces of Knossos and Zakros were used to store valuable ritual vessels. Here they were found empty. Next door, in the narrow rectangular room to the southeast, was found a clay tablet inscribed in Linear A and the famous "Phaistos Disc" bearing hieroglyphic writing. The building was therefore named the Palace "Archive" The building east of the Archive is thought to be a shrine or the archivist's residence, while the easternmost building is known as the "Potter's Workshop" because a large number of unfinished pots were found there. The intermediate building has an impressive peristyle of alternating pillars and columns. A staircase on the south side of the peristyle building connects the whole complex to the NE entrance to the Palace, which stood in this spot. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 31.6km (SE) The east part of the North Wing forms the workshop area of the Palace. It consists of the East Court and a complex of small rooms which are believed to be the workshops of the New Palace (1700-1450 BC). Approximately in the centre of the court are the ruins of a horseshoe-shaped kiln. The elongated rectangular building with 6 rooms on the west side of the court appears to have been used for the workshops of the kiln craftsmen. The square room on the north side of the court was the gatehouse of the northeast entrance to the Palace. It has gypsum slab flooring and benches around the walls. Behind it is a long corridor leading to the inner courtyard of the North Wing and thence to the "Royal Apartments" Image Library
 Messara, South - West Iraklion at 31.9km (SE) Matala (GR: Μάταλα) was the ancient port of Phaistos and Gortys and a former fishing community which has developed into a modern holiday center. It is located 4 km south-west of the village of Pitsidia and 75 km from Iraklion. It is built on the coast line of the Messara bay inside a small and picturesque inlet. During the 60's the caves of Matala were hosting a hippie commune.
 Messara, Iraklion South at 31.9km (SE) The village of Pitsidia is located 65 km southwest of Iraklion at an altitude of 80 m a.s.l, just before the magnificent bay of Messara. The village with aproximately 700 inhabitants is the oldest village of the area and is refered (by S. Spanakis) that it was the place where the soldiers of Nikiforos Fokas, commander of the Byzantine army, settled. The army, famous for its bravery, came from Pisidia of the south Asia Minor, and this is probably the origin of the name Pitsidia.
Image Library
 Milopotamos, Rethymno at 32.4km (E) Anogia is a mountain town with 2500 permanent residents and is 55 km away from Rethymnon and 36 km from Iraklion. The name Anogia, means "high place - Ano Gi", is connected with the location that is built, in altitude of 700 m. Hospitable and pleasant residents have to tell a lot of old stories that have marked the tradition and the culture of the village. Anogia is a well-known village historically for its resident's resistance to the conquerors, Turkish and Germans.
Image Library
 Matala, South - West Iraklion at 32.4km (SE) The Red beach is located around 700m south from Matala. It is a beautiful secluded beach with fine reddish sand originating from the rocks of the area. The name "Red Beach" is given by the visitors due to its reddish color while its original name is Ammoúdia (GR: Αμμούδια). The sea gets a lovely blue-green color, making the landscape really unique. The only way to access Red Beach is on foot or by boat from Matala. The walk from Matala takes about 20 minutes and it can't be considered as an easy one. Red Beach however can get pretty crowded in the high season. There is a small stone-wall canteen offering snacks and drinks and a few umbrellas and sun-beds. Nudism is tolerated at the two ends of the beach. Image Library
 Zaros at 32.6km (E) This is one of Crete's most famous monasteries. It played an important role during the years of the Cretan Renaissance, both in the letters and the arts, and, during the last centuries of Venetian rule, it was known for its many scholars, artists and venerable monks.
 Sfakia, White Mountains at 32.7km (W) It is located at an altitude of 750 m, 50 km SE from the city of Hania and 20 km from the village of Vryses. Its population is approximately 500 people. The small villages that constitute the community of Askifou are Kares, Ammoudari, Goni and Petres. The most touristic organised of them is Ammoudari with restaurants, gas station, and some rooms for rent.
 Cretan Singer and lyra player from Anogeia at 32.8km (E) Nikos Xylouris (Greek: Νίκος Ξυλούρης, 7 July 1936 - 8 February 1980), nicknamed Psaronikos (Greek: Ψαρονίκος, "Grey Nick"), was a Greek composer lyra (Cretan lyre) player and singer from the town of Anogeia. He was part of the movement that brought down the Greek military Junta of 1967. His songs and music captured and described the Greek psyche and demeanor, gaining himself the title the archangel of Crete. Image Library
 Moires, Messara at 33km (SE) The monastery of Panagia Kaliviani is located at the 59th km on the road Iraklion-Phaistos. The monastery was built during the second Byzantine period. The small Byzantine chapel was painted with frescoes but most of them are today destroyed. The chapel was deserted until, during the Turkish occupation in 1873, an old small icon of the Annunciation of the Holy Mother was miraculously found there.and the monastery became a place of worship.  Idi mountain at 33.1km (E) Located at the top (1750m) of Skinakas mountain of Idi (Ida) mounatin range, 60km from Heraklion. There are two telescopes and modern equipment and facilities both for research and educational activities in astronomy. It is a department of the University of Crete. Skinakas observatory offers a number of open days each year. This gives the opportunity to visitors to be introduced to the operation of the observatory, to get informed about the latest achievements in Astrophysics and to observe through the telescope. Open days for the year 2012: August 26 September 23 During the open days the Observatory facilities can be visited from 17:00 to 23:00. Due to low temperatures at the Skinakas altitude, warm clothes are highly recommended. The visitors will have the opportunity to be guided through the Observatory's infrastructure and follow a related presentation. The road to Skinakas Observatory is very narrow. Accident may occur and the space is limited on the top. For the reasons above, buses are not allowed (advised) to visit the Observatory during open days. Website : http://skinakas.physics.uoc.gr/  Sfakia, South Hania at 33.2km (W) The ravine begins from the last houses of the village of Imbros and 8 km after it ends at the village of Komitades. Its crossing is smooth and entails no danger...
 Sfakia, Hania, Crete at 33.2km (W) At the exit of the ravine of Imbros, near the south coast of Sfakia. It is located at an altitude of 200 m, 68 km from the city of Hania and 4,5 km from Hora Sfakion. The area is covered with olive trees and the view to the Libyan sea and the island of Gavdos in the horizon...
E4 Trail: 16. Trail: A rest day in Askyfou
by Richard Ellis at 33.4km (W) 29th August - Nicholas Crane, at the beginning of his huge walk across the watershed of Europe, writes that Julius Caesar and his Roman Army probably had it right when they walked for three days and rested for one. He ignored the advice (to his regret) and so did I in Part One, but now I had learnt my lesson. So for my rest day, I went for a little 7 km walk around the Askyfou plateau (without a pack) and found my way up to the Turkish fort which dominates the skyline there.
|
|||
|
| |||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S